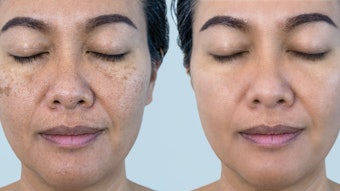
Micro-dosing treatment is a growing trend in skin care. It involves using formulas with a small percentage of concentrations, to gently train skin without breaking ties with barrier health. An article from Mind Body Green discussed the pros and cons.
Related: Synbiotic Supplementation Reduces Severity of Melasma
Micro-dosing skin care is the same as any other substance: instead of large use over a short amount of time, treatment would include low concentrations of active ingredients daily. Another method of micro-dosing would be using smaller amounts of products with a standard concentration.
It is meant to be a more gradual process to achieve results with powerful skin care ingredients like retinoids, AHAs and BHAs.
Those with sensitive skin or a weakened barrier can especially benefit from micro-dosing, as their skin is more prone to irritation and dryness. With micro-dosing, they can use more potent skin care ingredients without stripping their skin.
It can also be useful to warm up or prepare the skin for further treatment at a higher dose, but it may not produce the intended results until a higher dose is achieved.
Cynthia Bailey, M.D., dermatologist, and founder of Dr. Bailey Skin Care, says skin care ingredients can be looked at with a dose-responsive curve, which argues that no therapeutic benefits of the medicine are active until a certain dose is reached, then once the maximum effect is increased, any increased doses can lead to side effects instead.
Retinoids are popular for their collagen production and effectiveness at easing signs of aging. A high-strength retinoid product is considered to have a concentration of 0.3 to 1%.
Bailey says retinoids have benefits to skin besides collagen synthesis that could be activated at lower doses, including improved skin texture and tone.
Many AHAs are formulated at concentrations of 10% or higher, which some may find too irritating for their skin. Both glycolic and lactic acid can also be effective at 8% concentrations, according to the article.
As for BHAs, those products typically have a 0.5 to 2% concentration. Bailey considers 0.5% to be a micro-dose.
Sensitivities to vitamin C are relatively rare, but L-ascorbic acid (the most active form of vitamin C) can cause irritation in hypersensitive skin. A concentration of at least 8%, but not higher than 20%, of vitamin C, has been considered most effective for stimulating collagen synthesis.
With a micro-dose lower than that, there still may be an antioxidant benefit, but according to Bailey, it would be better to use a full dose of other antioxidant-laden ingredients for that effect.
Even with a micro-dose, there is still a chance to react poorly from an allergy or skin reaction, and micro-dosing multiple products with the same active ingredient would undo the concept altogether.
The goal of micro-dosing is to eventually work up to full concentration, using the micro-dosing as a gateway to transition the skin to full treatment.
It is highly recommended to never micro-dose sunscreen.