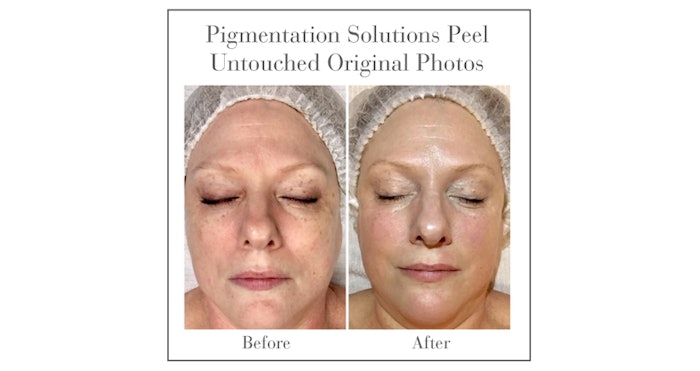
The skin is one of the body’s most dynamic organs with several unique characteristics––chief among them, pigmentation. The skin’s melanin determines the color and protects against UV damage.
Many individuals battle some form of a pigmentation and no skin is immune to this regardless of age, race or gender. This brings many challenges when trying to solve and determine a solution.
When a pigmentation issue occurs, how do you help restore the skin to a healthy, bright and glowing complexion?
Identify the Disorder Type
Like many functions within the skin, the process of creating pigment (melanogenesis) is extremely complex. When damaged, the melanin production process changes, either overproducing or slowing. This is when issues occur, resulting in one of three types of pigment changes:
- Hyperpigmentation––darkened pigment
- Hypopigmentation––a lack of melanin in the skin
- Demarcation––uneven pigment
While there are numerous factors that can disrupt the pigmentation process, there are typically three common triggers these can be traced back to, including:
- UV exposure
- Hormone fluctuations
- Inflammation
UV exposure is the number one cause of hyperpigmentation. Sun exposure increases the tyrosinase enzyme, and in excess, it can increase melanocyte activity. Eventually mutations in the melanocyte will stimulate excess melanin production. Hormonal fluctuations also trigger tyrosinase through the Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH). This often displays as melasma and can be further stimulated by inflammation and UV exposure. Finally, inflammation will increase histamines, Langerhans cells and melanin production and can lead to pigment being trapped in the papillary layer.
Solving the Pigmentation Issue
There are four critical factors to eliminating, reducing and managing pigmentation issues. These include:
- Surface exfoliation
- Suppression of melanocyte activity
- Skin lightening and brightening
- Cellular repair and protection
Professional treatments and a prescribed home care plan comprising intelligent ingredients will address these areas. Ingredients include:
- Daisy flower extract
- L-ascorbic acid
- Alpha arbutin
- Kojic acid
- Epilobium angustifolium flower (willow herb)
- Lotus extract
- Aminobutyric acid (GABA)
In the treatment room, a lotus-infused enzyme, mandelic acid and LED therapy will reduce pigment and brighten skin tone and provide a gentle, yet effective exfoliation. A luminescent gel mask containing plant stem cell technology and flower essences will restore, cool and hydrate. Oxygen, used with a serum containing niacinamide, magnesium ascorbyl phosphate (MAP) and vitamin B5, will drive nutrients deep into the skin to restore vitality.
For deeper exfoliation, TCA with sake and potent melanin suppressors will tone and refine the skin for a luminous, healthy complexion. Flower acids and mandelic acid will also brighten and stimulate cellular turnover. Follow with a vitamin A and peptide peel formula to rejuvenate damaged cells.
For home care, look to botanical brighteners, retinaldehyde, plant stem cells, epidermal growth factor and peptides. This combination will address the four key areas: exfoliation, melanin suppression, skin brightening and cellular repair and protection.
Disclaimer:
The above paid-for content was produced by and posted on behalf of the Sponsor. Content provided is generated solely by the Sponsor or its affiliates, and it is the Sponsor’s responsibility for the accuracy, completeness and validity of all information included. Skin Inc. takes steps to ensure that you will not confuse sponsored content with content produced by Skin Inc. and governed by its editorial policy.